Production RegionsPrimarily produced in northeastern China and the Korean peninsula.
Macroscopic FeaturesMain root is fusiform or cylindrical, 3~10cm long, 1~2cm diameter. Externally translucent, reddish-brown, sometimes with opaque dark yellowish-brown spots, with longitudinal grooves, wrinkles and thin root scars; upper portion has interrupted indistinct rings, lower portion has 2~3 twist-crossed lateral roots, with curved rootlets or remnants rootlets. Rhizome (“neck”) is 1~2cm long, apex has numerous indented stem scars (“bowls”), sometimes has 1~2 intact or broken adventitious roots. Hard and brittle texture, fractured surface is smooth and horn-like. faint distinctively aromatic odor; sweet and slightly bitter taste.
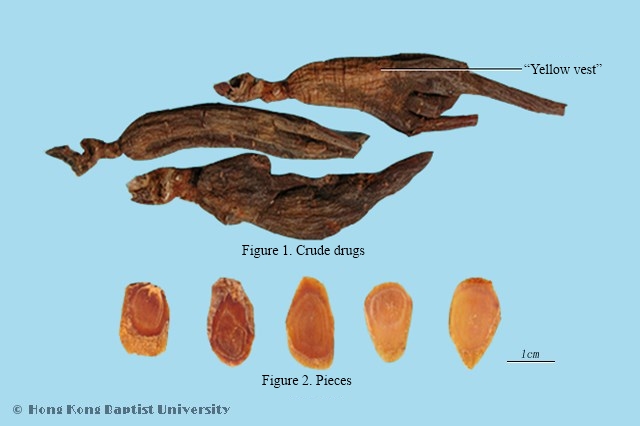
Quality RequirementsSuperior medicinal material is intact, thick, hard, with ‘yellow vest’.
PropertiesSweet, slightly bitter; warm.
FunctionsGreatly supplements original qi, secures desertion, engenders fluid, calms spirit. Apply to injury due to exhaustion, lack of food intake, lassitude, nausea and vomiting, loose of stools, cough due to deficiency and panting, sweating and acute prostration, palpitate with fear, amnesia, dizziness and headache, impotence, frequent urination, diabetes, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, infantile convulsions, discovery of chronicly deficiency, and all the diseases of deficiency of qi and blood and fluid.
Technical Terms'Yellow vest’: This refers to an earthy-yellow color that can be seen on the surface of the root body in relatively mature ginseng; its name comes from its appearance, which is like a yellow vest (Mandarin jacket) upon the root body. It is sometimes produced during the secondary processing of red ginseng.
OriginThe dried root and rhizome of Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.(Araliaceae)