Production RegionsPrimarily produced in the Chinese provinces of Guangdong, Guangxi, Fujian, Yunnan.
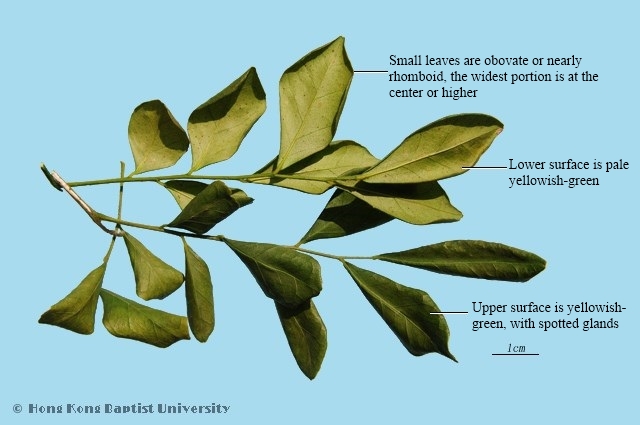
Macroscopic FeaturesMurraya exotica L.: Tender branches are cylindrical, 1~5mm in diameter, externally grayish-brown, with longitudinal wrinkles. Pliable texture, not easily broken, uneven fractured surface. Pinnately compound leaves have 3~9 leaflets, which have often fallen off; leaflets are obovate or nearly rhomboid, the widest portion is at the center or higher, about 3cm long, 1.5cm wide; apex is blunt, acute pointed or indented, base is slightly oblique, entire leaf; yellowish-green, thin membranous, upper surface has transparent spotted glands, leaflets have short or absent stems, lower portion is sometimes covered with soft hairs. Aromatic odor; bitter, acrid taste, with numbing tongue. Murraya paniculata (L.) Jack.: Leaflets are oval or elliptical, the widest portion is at the center or lower, 2~8cm long, 1~3cm wide; apex is gradually pointy or short pointed.
Quality RequirementsSuperior medicinal material has numerous leaves, green color, potent aroma.
PropertiesAcrid, slightly bitter; warm; little toxic
FunctionsMoves qi, stops pain, boosts blood, disperses stasis. Apply to stomachache, wind-damp impediment, externally used to toothache, injury from falls, snake and insect bites.
OriginThe dried leaves and leaf-bearing tender branches of Murraya exotica L., and Murraya paniculata (L.) Jack. (Rutaceae)