Production RegionsPrimarily produced in the Chinese provinces of Anhui, Jiangsu, Henan, Hebei.
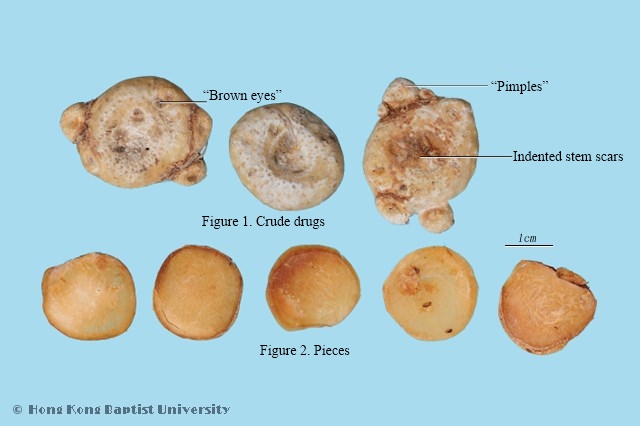
Macroscopic FeaturesFlat spherical shape, 1~2cm tall, 1.5~6.5cm diameter. Externally off-white or pale brown, relatively smooth, apex has indented stem scar, edge has pitting root scars, and sometimes with small spherical lateral sprouts on the edge. Firm texture, hard to break, fractured surface is uneven, white, powdery. Slightly acrid odor, spicy taste.
Quality RequirementsSuperior medicinal material is large, powdery, white.
PropertiesBitter, acrid, warm, toxic
FunctionsDries dampness, transforms phlegm, dispels wind, calms fright, eliminates swelling, disperses binds. Apply to stroke and hemiparalysis, epilepsy, infantile convulsion, tetanus, injuries and fractures from falls, bites by snakes and insects.
Processed FormGinger nan xing (processed nan xing): clean tian nan xing, graded by sizes, soak in water, change water 2~3 times a day, if there is white foam, then add some bai fan after changed the water (every 100kg tian nan xing need 2kg bai fan), after one day of soaking, then change the water again, until the cut opening is slightly numbing tongue, take out tian nan xing, processed with sheng jiang and bai fan, 12.5kg each. After procced, the toxic nature is reduced. Dan nan xing: use the processed nan xing, add some clean bile (or bile paste powder and some water), evenly stir, completely steam for 60 min, take out and cool, cut into small clusters, and dry. Or use unprocessed tian nan xing powder, add clean bile (or bile paste powder and some water), evenly stir, put in warm position, let it ferment for 7~15 days, steam or steam mediated by water for 9 days, stir every 2h, eliminates the fishy evil odor, until it becomes black paste, has no numbing tongue when tasted, take out and cool. Resteam to make it soft, and cut into small clusters, and dry. Every 100kg of dan nan xing powder need 400kg of cattle (or pig) bile (or 20kg bile paste powder). Clears heat, transform phlegm, extinguishes wind, calms fright; apply to heat phlegm and cough, yellow and thick phlegm, phlegm stasis and stroke, convulsion and fright.
Technical Terms'Brown eyes’: This refers to indented stem base scars seen on rhizome medicinal; these are enriched by numerous spots of rootlet scars, which are also called ‘measles spots (ma dian)’. ‘Pimples’: this refers to raised spots on the surface. Due to differences between medicinal materials, “pimples” refer to a variety of different botanical features. In the case of tian nan xing, it refers to protrusions from round sprouts.
OriginThe dried tuberous rhizome of Arisaema erubescens (Wall.) Schott or Arisaema heterophyllum Bl.(Araceae)