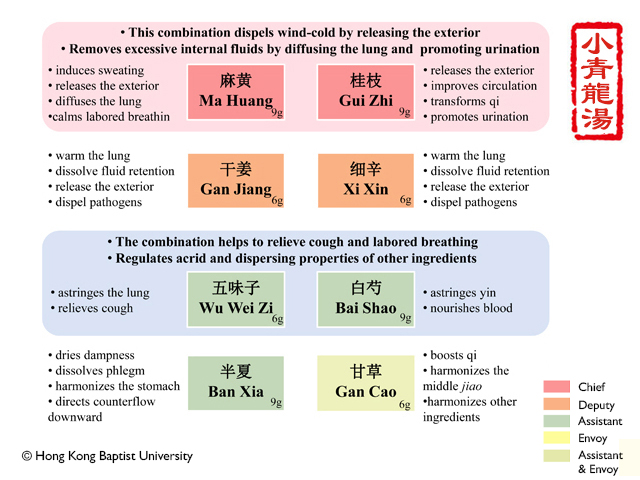
| Chief | Ma Huang |
| Removes excessive internal fluids by diffusing the lung and promoting urination. |
| Chief | Gui Zhi |
| Removes excessive internal fluids by diffusing the lung and promoting urination. |
| Deputy | Gan Jiang |
| |
| Deputy | Xi Xin |
| |
| Assistant | Wu Wei Zi |
| Regulates acrid and dispersing properties of other ingredients. |
| Assistant | Bai Shao |
| Regulates acrid and dispersing properties of other ingredients. |
| Assistant | Ban Xia |
| |
| Assistant&Envoy | Gan Cao |
|