NameCenter-Supplementing and Qi-Boosting Decoction
ClassificationTonic formulas
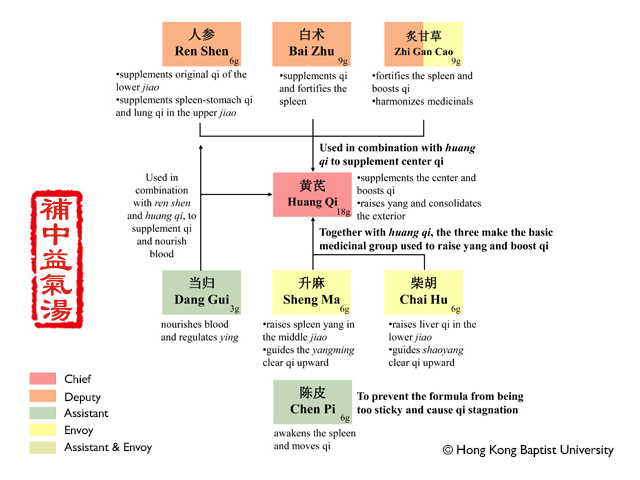
CombinationAstragali Radix (Huang Qi) 1 qian (18g), Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma Praeparata cum Melle (Zhi Gan Cao) 5 fen (9g), Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma (Ren Shen) 3 fen (6g), Angelicae Sinensis Radix (Dang Gui soaked in wine and dried) 2 fen (3g), Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium (Chen Pi) 2 or 3 fen (6g), Cimicifugae Rhizoma (Sheng Mao) 2 or 3 fen (6g), Bupleuri Radix (Chai Hu) 2 or 3 fen (6g), Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma (Bai Zhu) 3 fen (9g)
MethodIn the original text, it was noted, “add two cups of water and boil until it is decocted into one cup. Take it while it is warm.” Modern administration: decoct with water. It can also be made into pills. Take ten to fifteen grams each time, two to three times a day. Take the pills with warm boiled water or ginger soup.
ActionSupplements the center and boosts qi; raises yang and lifts the sunken.
IndicationBu Zhong Yi Qi Tang is indicated for two patterns. The first pattern is deficient or sunken spleen qi with reduced food intake, general sluggish sensation, weak breathing, lack of desire to speak, sallow-yellow facial complexion, and loose unformed stool. The tongue is pale and the pulse is deficient. It is also used for rectal prolapse, uterine prolapse, chronic diarrhea, and flooding and spotting (beng lou). The second pattern is objective or subjective fever due to qi deficiency manifested by a feverish sensation, spontaneous sweating, thirst with a desire for hot drinks, shortness of breath, and lack of strength. The tongue is pale and the pulse is deficient, big, and weak.
PathogenesisThe etiologies involved are an improper diet and exhaustion-fatigue (fatigue from overstrain). Pathogenic factors damage the spleen-stomach causing deficiency, which over time, lead to sinking of clear yang. The spleen-stomach is the generating source of ying, wei qi, qi, and blood. Reduced food intake, weak breathing, lack of desire to speak, loose, unformed stool, etc. are all signs of spleen-stomach deficiency. Rectal and uterine prolapse indicate spleen deficiency. The spleen governs the ascent of the clear and when it is deficient over a period of time will lead to center qi sinking. Feverish body and spontaneous sweating are caused by deficiency of qi, which fails to consolidate the exterior and floats (yang) to the external part of the body. The treatment principle should be to supplement spleen-stomach qi, and raise the sinking yang.
ClarificationThe feverish body (fever) in this pattern is caused by qi deficiency rather than external contraction. Deficient spleen and stomach qi fails to ascend and descend normally. As a result, the clear yang sinks and spleen dampness flows downward. Long-term accumulation of yang qi in the lower jiao generates heat, which then stirs upward.《Clarifying Doubts about Damage from Internal and External Causes》teaches that to treat this kind of fever, “the only method is to supplement the center qi and raise yang with sweet-warm medicinals and to clear the fire with sweet-cold medicinals. This type of fever can only be relieved by warm medicinals. Bitter-cold medicinals should be prohibited for use at this moment, for they would do harm to the spleen-stomach. This is the reason for the development of Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang.” The sunken yang fails to rise and becomes stagnant. As such, it fails to spread to the exterior and causes fever. Sweet-warm medicinals boost qi and raise the yang so clear yang can return to its original place and allow the fever to automatically disappear. Therefore, Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang is regarded as the representative formula to “clear heat with sweet-warm medicinals.”
Application1. Essential pattern differentiation Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang is a representative formula used to boost qi, raise yang, and clear heat with sweet-warm medicinals. This clinical pattern is marked by general sluggishness, lack of strength, weak breathing, less desire to talk. 2. Modern applications Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang is widely used to treat the following diseases caused by spleen-stomach qi deficiency or center qi sinking in terms of TCM: visceroptosis, chronic diarrhea, prolapse of organs (uterus, anus), myasthenia gravis (MG), chyluria, chronic hepatitis, urinary retention during pregnancy or the postpartum period, threatened miscarriage, profuse menstruation, drooping eyelid, and paralytic strabismus. 3. Cautions and contraindications This formula is prohibited for patients with yin-deficiency fever or excessive internal heat.
Additonal formulae1. Sheng Yang Yi Wei Tang (Yang-Raising and Stomach-Boosting Decoction 升陽益胃湯)
RemarkGinseng ( Panax ginseng ) is listed in the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) Appendix II. Its trade is allowed but subject to licensing controls.
Source《Clarifying Doubts about Damage from Internal and External Causes》Nei Wai Shang Bian Huo Lun《內外傷辨惑論》