Largehead Atractylodes Rhizome
Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma
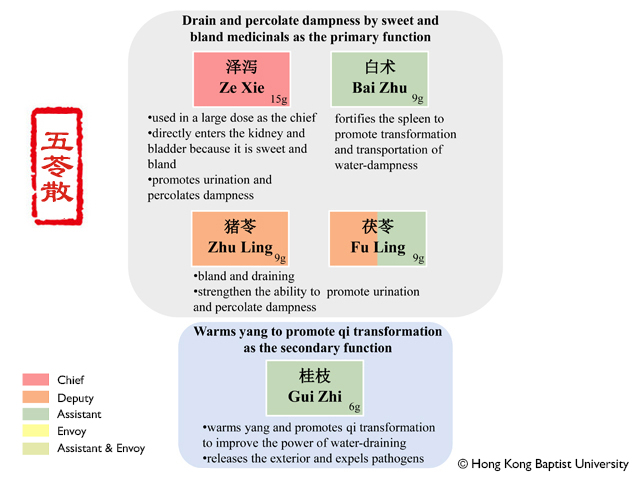
Functions:Fortifies the spleen, boosts qi, dries dampness, promotes urination, stops sweating, calms the fetus. Apply to deficiency-weakness of spleen, anorexia, and abdominal distension, and loose tools, dizziness induced by phlegm and retained fluids, edema, spontaneous perspiration, restless fetal movement.